Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
MODEC declares its support for the Recommendations of TCFD (the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures). Fulfilling our mission to secure the stable supply of energy, we contribute to achieving global goals of "Realization of a low or zero carbon society" guided by the SDGs and the Paris Agreement in cooperation with governments, other companies, and local communities.
Governance Framework for Climate Change Response
MODEC manages climate change risk and its response based on its internal governance framework of ERM (Enterprise Risk Management). We have selected climate change as one of the ERM "Significant Risks", which are the risks to be managed with special attention due to the particularly significant impact on management without sufficient countermeasures. Executive Officer in charge of Corporate Planning & Strategies is responsible for the management of ERM process, and Board of Directors (BOD) and Management Board (MB) as well as President & CEO regularly receive reports regarding the Significant Risks, monitor and supervise the progress and the implementation results of the responses.
Selected Scenarios
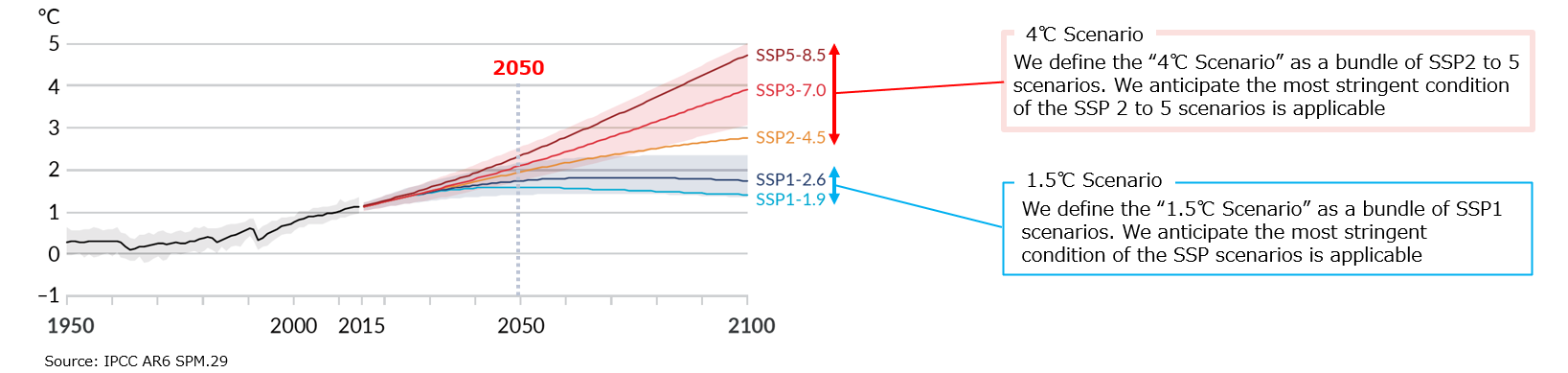
We have determined two scenarios with range, based on SSP scenarios*1.
Published scenarios and their analyses*2 are reviewed to develop the worldview of each scenario.
- Forecast of global averages surface temperature(Difference from the 1850-1900 average)
-
-
- *1 "Shared Socioeconomic Pathways", scenarios of projected socioeconomic global changes up to 2100, which was used in IPCC 6th Assessment Report on climate change published in August 2021.
- *2 Below 8 scenarios are reviewed for our climate-related assessments.
- IEA: Stated Policies Scenario/ Announced Pledges Scenario/ Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario
- Bloomberg NEF: Green Scenario/ Gray Scenario/ Red Scenario
- DNV: Energy Transition Outlook/ Pathway to Net Zero
Worldview Assumed in the Scenario Analysis
We have assumed the following two worldview as of 2050 in the scenario analysis.
| 4℃ scenario | 1.5℃ scenario | |
|---|---|---|
| Overview | Physical risk increases as low-carbon/ decarbonization trends weaken and demand of fossil fuels and upstream investments remains. | Expansion of carbon regulations and other policies result in establishment of renewable energy and increase of investment in low-carbon technologies: World where both renewable energy and low-carbon are firmly established. |
| Government |
|
|
| Changes in the energy market |
|
|
| Energy companies (Customers) |
|
|
| The floating production system industry |
|
|
| Financial institutions/ Investors |
|
|
| Physical risk |
|
|
| New entrants/ Substitutes |
|
|
Major Risks and Opportunities Associated with Climate Change
The evaluation of climate change risks and opportunities is an ongoing process. It is key to identify and manage the risks imposed by the climate change. At MODEC, we have conducted initial evaluation of business to map potential risks and opportunities using TCFD methodology.
TCFD defines two types of climate risks: transition risks and physical risks.
Transition and physical risks can significantly impact businesses' financial performance and sustainability. Therefore, we have assessed and disclosed our exposure to these risks as part of climate-related financial disclosures.
- Transition Risks
- These risks arise from the transition to a low-carbon economy, such as policy and regulatory changes, technological advancements, and shifts in consumer preferences. In addition, transition risks can impact businesses through changes in market demand, the availability and cost of resources, and changes in the competitive landscape.
| Potential Risks | Scenario | Business Impact | Short /Mid |
Long | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policies, laws, regulations |
Carbon Pricing | 1.5/4 |
|
||
| Regulatory | 1.5 |
|
|||
| Market | In the energy mix change | 1.5 |
|
||
| Reduction of oil & gas demand | 1.5 |
|
|||
| Technology | Pressure to develop next-generation technologies and spread of low-carbon technologies in a short term | 1.5 |
|
||
| Reputation | Negative societal evaluation of the oil & gas industry | 1.5/4 |
|
||
Financial |
Changes in financing accessibility due to new climate-related requirements | 1.5 |
|
||
| Employees attraction and retention | Lack or reduction of interest of skilled professionals to work for the oil & gas industry | 1.5 |
|
||
- Physical Risks
- These are risks arising from the physical impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events, sea level rise, and heatwaves. Physical risks can impact businesses directly or indirectly through supply chains or the communities in which we operate. These risks may affect different dimensions of MODEC value chain. The table below shows potential impacts of physical risks to our business.
| Potential Risks | Scenario | Business Impact | Short /Mid |
Long | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute | Extreme weather conditions | 4 |
|
||
| Chronic | Rising mean temperatures/ Changes in rainfall and weather patterns/ Rising sea levels | 4 |
|
||
- Opportunities
- Efforts to mitigate and adapt to climate change also produce opportunities. The table below shows potential opportunities to our business. The areas of opportunity are based on the TCFD recommendations.
| Potential Risks | Scenario | Business Impact | Short /Mid |
Long | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Energy sources |
Use of reusable energy |
1.5/4 |
|
|||
| Products/ Services |
Technology | Expansion of the renewable energy business | 1.5/4 |
|
||
| Spread of low-carbon technologies | 1.5/4 |
|
||||
| Developing next-generation technologies |
|
|||||
| Market | In the energy mix change | 1.5/4 |
|
|||
| Policies, laws, regulations | Carbon pricing and carbon emission targets/ policies of each country | 1.5/4 |
|
|||
| Other opportunities | 1.5/4 |
|
||||
Forecasted Impacts
We have made a preliminary evaluation on the degree of business impacts of risks and opportunities in 1.5℃ Scenario: While the market may shrink, business is expected to expand by decarbonizing technologies and new market creation.
This is our initial evaluation, and further evaluation will be implemented continuously as uncertainties associated with outcomes under the scenario are more assessed based on related information and data that may be updated or become available in the future.
![]()
| Risks and Opportunities | Short and Mid Term | Long Term |
|---|---|---|
| Increased cost due to the introduction of Carbon Pricing |  |
*1 |
| Shrinkage of the market due to the decline of fossil fuel demand | 
|
|
| Expansion of the market share because of the decarbonizing technologies for our FPSOs |  
|
|
| New market creation by new technologies | 
|
 
|
| Limitation to access finance and increased financial cost for the business related to fossil fuels | 
|
- *1 It is assumed that increased cost will be borne by clients.
Targets and Roadmap
Diligently pursuing Business Model Evolution, MODEC aspires to achieve Net Zero by 2050
Stable supply of energy has been our dedicated purpose for more than half a century.
Now we take steps towards "stable" and "sustainable" supplies of energy, endeavoring to be a bridge towards the future.
By leveraging our strengths and competencies, we will play two key roles in the energy transition.
A: Continuing contributions to stable oil and gas supply by FPSOs, while minimizing GHG emissions
B: Accelerating the business model evolution to contribute to clean energy generation
- Business Strategy
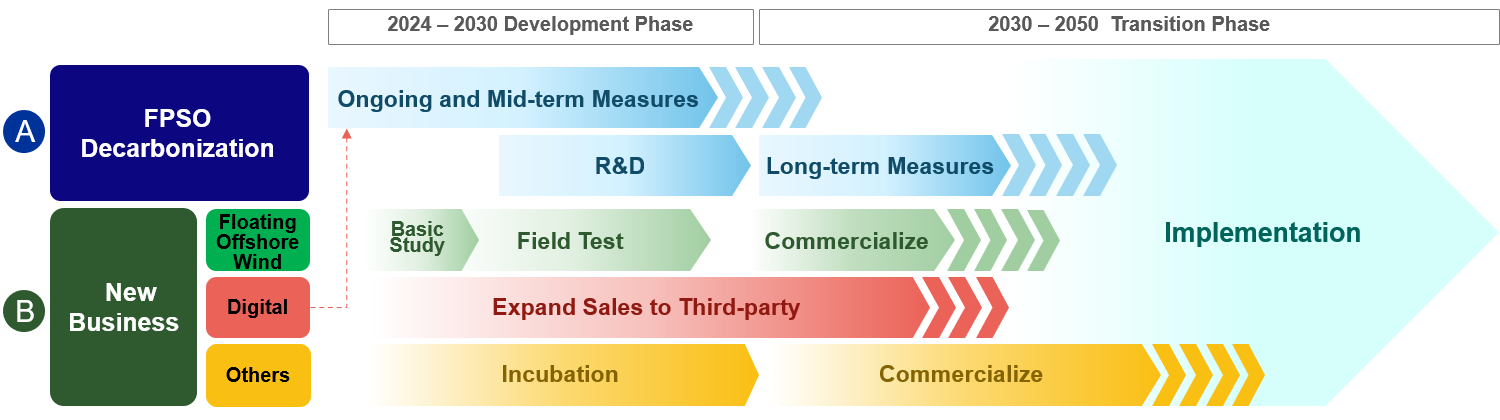
| FPSO |
"Ongoing" efforts toward stable and low emission FPSO |
 |
Asset Integrity Improvement |
| "Mid-term" measures (Implementing) | Energy efficient design (e.g. combined cycle) & hydrocarbon recovery | ||
| "Long-term" innovative measures (Developing) | Enables drastic reduction(e.g. post-combustion CCS, external power) | ||
| Next generation MODEC hull (Current development) | Enables of “Long-term” measures | ||
| FOW | Full-scale field test is being pursued | To be ready for commercialization by 2030 | |
| Penetration into Japan’s IPP market | 400MW class wind farm formation in early 2030’s and further expansion | ||
| Contribution to world’s floating wind industry | Leveraging floating solutions expertise & relationship with strategic clients | ||
| Digital | Contribution to MODEC FPSO’s decarbonization |
Advanced analytics technology that can reduce downtime and inefficiency | |
| Contribution to decarbonization of other companies | Improving 3rd party’s operation efficiency by application of our products | ||
| Others | Venturing into new business opportunities | Diversifying business portfolio along with the energy transition |
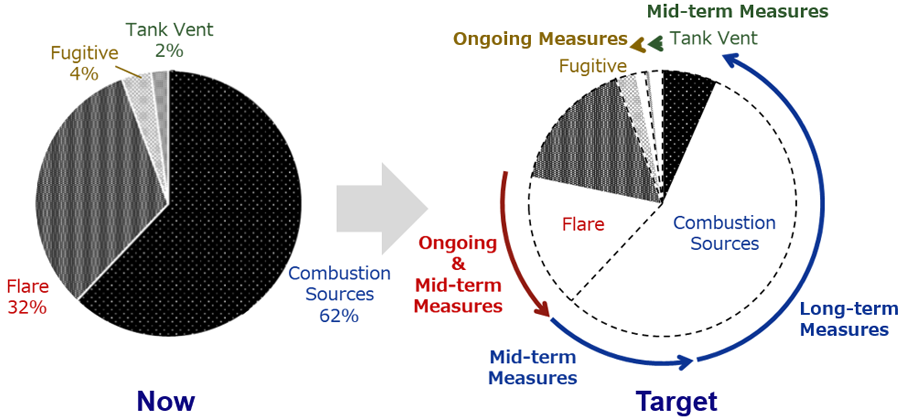
- FPSO Carbon Intensity
- We set "FPSO Carbon Intensity"* as one of strategic KPIs and aspire to reduce it drastically.
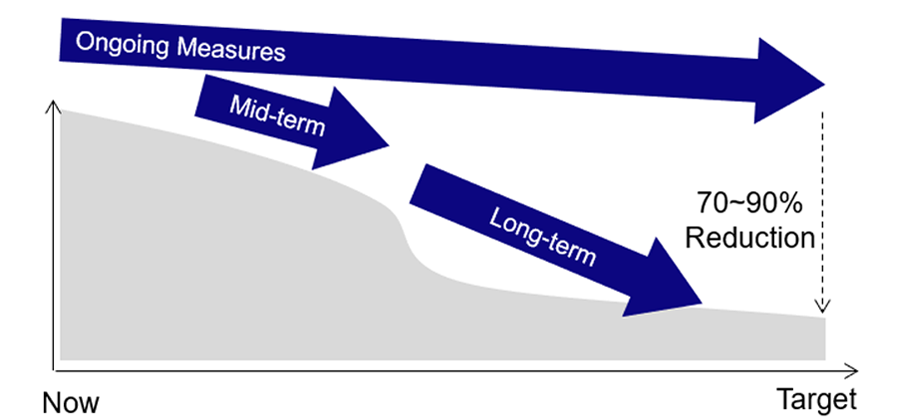
- *tons-Co2e per tons-Hydrocarbon
- Pathway Toward Net Zero 2050
- We aspire to achieve "Net Zero*1" by 2050 as a result of implementing above business strategy including FPSO decarbonization with significantly reduced FPSO Carbon Intensity and New Business Development.
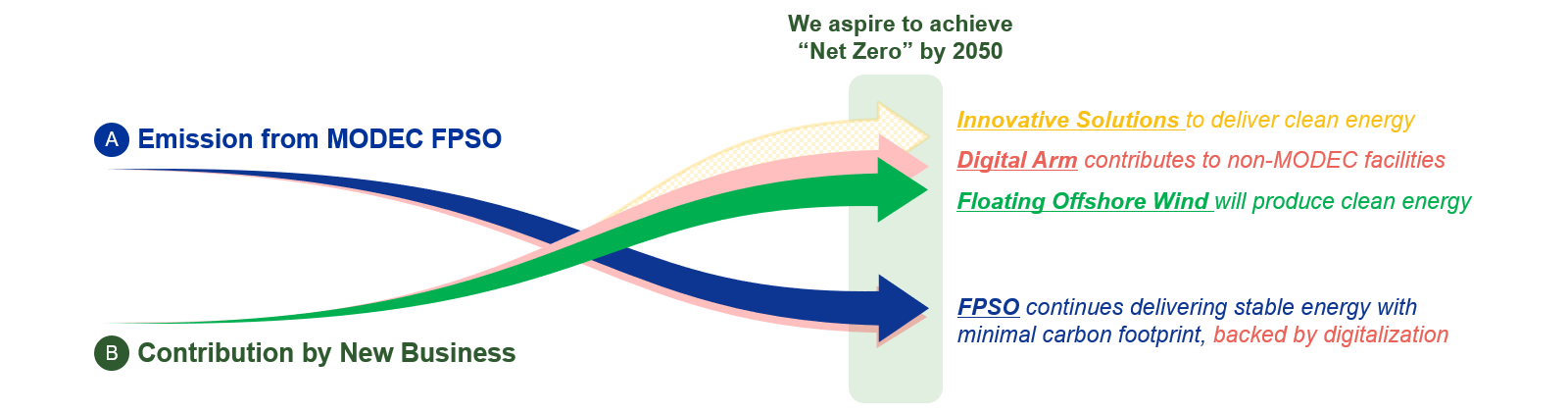
- *1
- The MODEC GHG emissions in Scope 1, Scope 2 and Scope 3 (Category 13 - Downstream Leased Assets only) are to be reduced, and residual emissions are to be offset by GHG reduction contribution through our New Business, for example, we consider generated electricity by FOW as relative reduction contribution against conventional energy.
- In the middle of above pathway, we target to achieve net zero for scope 1 and 2 only by 2030.
